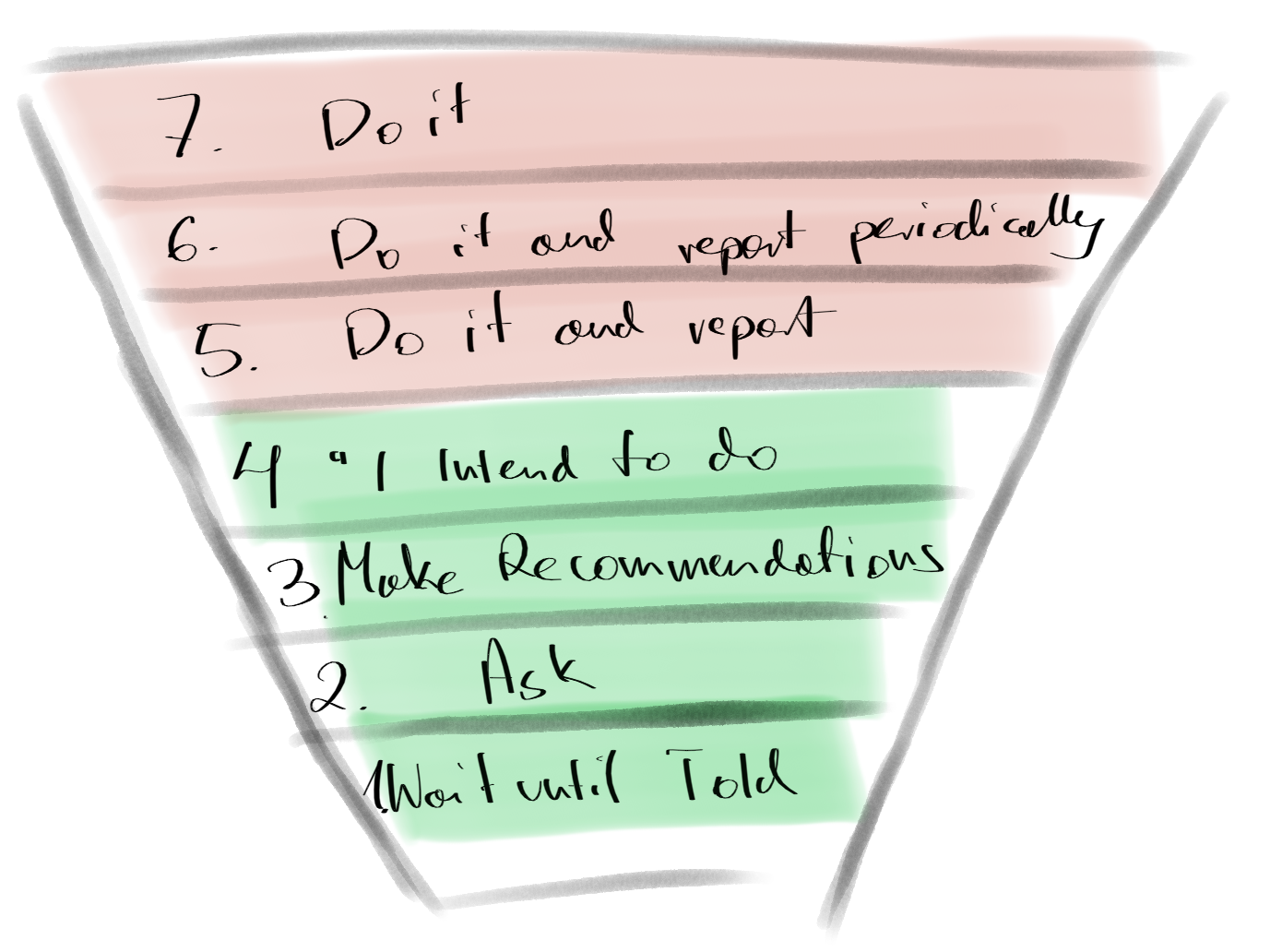
Critical Path - Your North Star for Predictable Project Delivery
Unlocking project predictability and empowering your engineering teams requires a right planning methods. This post dives deep into the Critical Path Method, a powerful concept that transforms how we manage projects, prioritize tasks, and achieve our delivery goals.
As engineering managers and developers, we’re constantly navigating the complexities of project delivery. We strive for efficiency, predictability, and ultimately, success. Yet, amidst the multitude of tasks, dependencies, and deadlines, how do we ensure we’re always focusing on what truly matters? The answer often lies in understanding and mastering the planning and project management techniques.
Here, you will learn about the fundamental principles of the Critical Path, its profound benefits for various roles within an engineering organization, practical steps to apply it.
What is a critical path?
Proper definition
The Critical Path is the longest sequence of dependent activities that determines the shortest possible duration for completing the entire project. It’s the series of tasks that, if delayed, will directly delay the entire project’s completion.
Intuitive definition
Imagine you are building a house. You have many tasks: laying the foundation, framing the walls, plumbing, electrical, painting, etc. Some tasks, like letting the concrete foundation dry or waiting for the walls to cure, take a fixed amount of time and cannot be rushed. In the meantime, you might be able to prepare the interior design, which has more flexibility.
The critical path would be the sequence of tasks that dictates how soon you can move into the house – for instance, if the wall drying takes longer, the entire move-in date shifts. It’s the path with no “slack” or extra time.
Why you need it?
Effective project planning, particularly Critical Path Method, can lead to different outcomes. While they might look similar, they might play different roles for different people at a different stage of the project.
Drill down on faster project delivery
By identifying the most time-sensitive tasks, teams can focus efforts and resources to accelerate the overall project timeline, and identify tasks that are crucial to be delivered on time.
Know when we can land the project
It provides a realistic and data-driven estimate of project completion, enabling more accurate forecasting and setting clear expectations with stakeholders.
Facilitates more effective resource management
Understanding which tasks are critical allows managers to strategically allocate their most skilled personnel to where they will have the greatest impact, preventing resource bottlenecks.
Helps avoid bottlenecks
You can also reveal potential choke points and dependencies, allowing teams to proactively address risks, implement contingency plans, and prevent delays before they occur.
Why people might need it?
Understanding how it impacts different stakeholders fosters better collaboration and alignment towards common project goals. Here is how different roles might see the tool:
Managers
It’s the backbone of your the schedule, highlighting the tasks that, if delayed even by a day, will push back the entire project’s completion date. It’s your North Star for prioritization, enabling effective resource allocation and risk mitigation.
Developers
It’s understanding which tasks are truly “on the critical path” – the ones where your focused effort has the most direct and immediate impact on the project timeline. It helps you see the bigger picture beyond your individual tickets, fostering a sense of ownership and purpose.
Product Managers
It is used for managing stakeholder expectations, and ensuring product features are delivered on time. It helps PMs understand the true timeline implications of scope changes and prioritize features that align with the critical path for market impact.
Directors
Provides high-level visibility into project feasibility and timelines, aiding in strategic decision-making and setting realistic organizational goals. It helps in assessing overall project health and resource capacity.
What is the high-level guide?
While tools can automate the process, understanding the typical steps to determine and manage the critical path is crucial:
- Break Down Project into Activities: List all necessary, distinct tasks or activities required to complete the project.
- Sequence Activities and Define Dependencies: For each task, identify its predecessors – the tasks that must be completed before it can begin. This establishes the logical order of operations.
- Estimate Activity Durations: Assign a realistic time estimate (e.g. days, or weeks) for each task’s completion.
- Diagram the Network: Create a visual representation showing tasks as nodes and dependencies as arrows connecting them, illustrating the flow of work.
- Calculate the Critical Path: Determine the start dates and end dates of the tasks. Identify tasks with zero free time – these tasks are on the critical path.
- Identify the Longest Path: Confirm the critical path as the sequence of tasks with the longest total duration, representing the shortest possible project completion time.
- Monitor and Update the Plan: Continuously track progress against critical path tasks. As the project evolves, dependencies change, or new information arises, be prepared to recalculate and update the critical path to maintain accuracy.
What tooling methods works?
There are numerous project planning tools available. While the tool can certainly enhance the process, the underlying methodology of critical path planning is far more important. You can effectively apply critical path principles even with basic tools like a document or an spreadsheet.
Here are some methods that have proven most effective in my experience:
Whiteboard
In the pre-pandemic era, when all teams worked collaboratively in the office, a whiteboard, meticulously led by a project manager or team lead, was often the best way to visualize and manage the critical path. The tactile nature of drawing tasks, dependencies, and estimated durations together fostered deep understanding and collective ownership within the team. It facilitated immediate feedback and dynamic adjustments, making it an incredibly effective tool for smaller to medium-sized projects.
Jira Plan
Today, with distributed and hybrid teams, tools like Jira Plan have become my primary tool. They allow for digitally mapping tasks, dependencies, and estimations, automatically calculating the critical path and providing dynamic updates as work progresses. Jira seamlessly integrates with existing engineering workflows and is easily scalable to manage work across many teams.
When to use this method?
While the critical path is a powerful tool, it’s most impactful when applied strategically:
- When a project involves two or more engineers, as dependencies and parallel work become complex, making critical path analysis vital for coordination.
- For projects spanning two or more months, as shorter projects might manage dependencies informally, but longer projects face increased risk of delays, making formal critical path planning essential for predictability.
- When project estimation is precisely needed, such as when marketing requires a definitive launch date to start a campaign, critical path analysis provides the rigor necessary to commit to and meet those deadlines.
Summary
Every tool, including critical path planning, can be used and misused. In a highly skilled environment, where engineers and managers already understand the basics of project execution, the critical path isn’t about micromanagement or pushing for unreasonable deadlines. Instead, it’s a framework for clarity, strategic focus, and empowering teams to make informed decisions. By embracing this methodology thoughtfully, we can foster a culture of precision, purpose, and unparalleled engineering excellence, delivering remarkable results together.